Return to U.S. Space & Rocket Center
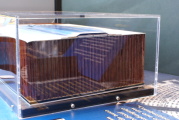
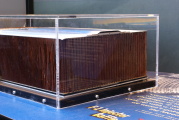
S-II Common Bulkhead Insulation
The LOX and LH2 tanks of the S-II stage shared a common bulkhead (rather than having more customary, hemispherical bulkheads separated by an intertank structure, as was done with the S-IC stage). By using a common bulkhead, North American was able to shorten the stage by about 10 feet and save nearly 4½ tons of weight.
The two tanks had to be insulated from each other to prevent the liquid hydrogen (at -423°) from freezing the liquid oxygen (which freezes at -362°). Thus, the aluminum sheets of the propellant containers were separated by a honeycomb insulation. This insulation was 5 1/8" thick at the forward end of the common bulkhead and tapered off toward the aft end.
The USSRC displays a chunk of S-II common bulkhead honeycomb insulation. The display was originally designed with a small lever to allow the visitor to lift the common bulkhead to see how light it was, but untold numbers of over-exuberant (and under-supervised) children put an end to the lever and so it is now a static display.
 dsc79617.jpg |
 dsc73944.jpg |
 dsc73941.jpg |
 dsc79615.jpg |
 dsc73943.jpg |
 dsc79616.jpg |
 dsc74878.jpg |
 dsc73955.jpg |
Return to U.S. Space & Rocket Center